The Truth: Are Ramen Noodles *Really* Bad For You? + Tips
Are Ramen Noodles a Silent Killer Lurking in Your Pantry? The truth about this seemingly harmless, budget-friendly meal could be more alarming than you think.
Ramen noodles hold a ubiquitous presence, particularly resonating with children due to their affordability, effortless preparation, and palatable taste. Yet, beneath this veneer of convenience lies a simmering concern regarding their purported health implications. Whispers even suggest a potentially deadly facet to this commonplace food.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Common Name | Instant Ramen Noodles |
| Potential Health Concerns | High sodium content, low nutritional value, processed ingredients, additives |
| Sodium Content Example | Up to 1,000mg per serving (significantly exceeding recommended daily intake for children) |
| Nutritional Deficiencies | Lacking in protein, fiber, essential vitamins, and minerals |
| Processing Concerns | Often made with refined flour, fried in unhealthy oils, containing trans fats |
| Additives Present | Preservatives, flavor enhancers (e.g., MSG), artificial coloring agents |
| Target Audience | Frequently marketed towards children through vibrant packaging and endorsements |
| Associated Health Risks | High blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, kidney issues, obesity, malnutrition, allergies, hyperactivity |
| Healthy Alternatives | Whole-wheat pasta, brown rice, quinoa, vegetable-rich soups |
| Website for Health Information | American Heart Association |
The assertion that ramen noodles directly incite mortality lacks substantive scientific confirmation.
However, a critical examination reveals a concerningly elevated sodium content. A solitary serving of ramen noodles can harbor as much as 1,000 milligrams of sodium. This constitutes over half of the recommended daily sodium intake for adult individuals. Excessive sodium consumption is a well-established precursor to hypertension, a condition that significantly amplifies the probabilities of developing cardiovascular ailments and strokes.
Furthermore, ramen noodles are nutritionally deficient. Their composition reveals a paucity of protein, fiber, and essential vitamins. Consequently, they offer minimal nutritional benefit. Over-reliance on ramen noodles in one's dietary regimen can precipitate malnutrition.
Should you harbor apprehensions regarding your child's well-being, a consultation with your physician is advisable to determine whether ramen noodles constitute a judicious dietary choice for them.
- Unleash The Roar Your Guide To The Lion King Telugu Movie Download
- Discover Chiara News Your Source For News And Information Today
Ramen noodles are a staple food, especially among younger demographics. They are inexpensive, convenient, and palatable. However, unease persists regarding their potential health detriments. Certain quarters have even asserted that ramen noodles possess lethal attributes.
- Sodium content: Ramen noodles exhibit high sodium levels. A single portion may contain up to 1,000 milligrams of sodium, exceeding half of the daily recommended intake for adults and predisposing individuals to hypertension.
- Low nutritional value: Ramen noodles lack essential nutrients, containing negligible amounts of protein, fiber, and vitamins. This translates to limited nutritional value and a risk of malnutrition.
- Processing concerns: Ramen noodles are crafted from refined flour, devoid of its innate nutrients, and frequently subjected to frying in deleterious oils.
- Additives: Ramen noodles incorporate various additives, encompassing preservatives, flavor enhancers, and artificial colors, some of which have been implicated in health complications.
- Portion size: Ramen noodles are commonly packaged in expansive quantities, fostering unintended overconsumption and a heightened risk of excessive sodium and unhealthy ingredient intake.
- Marketing to children: Ramen noodles are often marketed towards children, fostering the perception of their inherent healthfulness.
While concrete scientific validation of the assertion that ramen noodles induce death is lacking, awareness of the potential health risks associated with their consumption is paramount. Parents should educate their offspring on the significance of maintaining a balanced diet and making judicious dietary choices.
Ramen noodles are a staple food, particularly prevalent among children. Their appeal lies in their affordability, ease of preparation, and palatable taste. Nevertheless, reservations linger concerning their possible health ramifications, notably their elevated sodium content.
- High blood pressure: Excessive sodium consumption can precipitate hypertension, a major precursor to cardiovascular disease and stroke. Children afflicted with hypertension are at an elevated risk of developing persistent hypertension in adulthood.
- Other health problems: Elevated sodium intake can also contribute to other health problems, including kidney disease, osteoporosis, and gastric cancer.
- Children are more vulnerable: Children are more susceptible to the adverse effects of high sodium intake compared to adults due to their incomplete renal development and ongoing growth.
Given the substantial sodium content in ramen noodles and the attendant health risks associated with excessive sodium consumption, it is imperative for parents to remain vigilant and moderate their children's intake of ramen noodles.
Ramen noodles, a familiar comestible, particularly among younger generations, are celebrated for their affordability, swift preparation, and agreeable taste. However, apprehensions exist regarding their potential health implications, predominantly centered on their diminished nutritional value.
Ramen noodles, fabricated from refined flour stripped of its inherent nutrients, are often subjected to frying in unhealthy oils and exhibit a dearth of protein, fiber, and vitamins. Consequently, their nutritional contribution is limited, potentially culminating in malnutrition.
Malnutrition, a state arising from insufficient nutrient intake via the diet, can trigger diverse health adversities, encompassing stunted growth, impaired cognitive advancement, and weakened immune competence.
Children grappling with malnutrition exhibit heightened susceptibility to illness and learning impediments. Furthermore, they face an increased predisposition to chronic ailments, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
Considering the scant nutritional profile of ramen noodles and the potential health hazards linked to malnutrition, it is pivotal for parents to maintain awareness and circumscribe their children's ramen noodle consumption.
The processing methodologies inherent in ramen noodle production significantly amplify the potential health detriments associated with this food. Refined flour, characterized by the removal of its bran and germ (the most nutritionally replete components of the grain), exhibits diminished fiber, protein, and vitamin content. Furthermore, ramen noodles frequently undergo frying in deleterious oils, introducing trans fats into the dietary equation. Trans fats, an unhealthy lipid variety, can elevate LDL cholesterol levels and heighten the susceptibility to cardiovascular disease.
The confluence of refined flour and detrimental oils renders ramen noodles a suboptimal nutritional selection. Excessive consumption of ramen noodles can engender an array of health predicaments, including obesity, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. Children who heavily consume ramen noodles are also vulnerable to malnutrition, as this dietary staple fails to furnish the requisite nutrients for proper growth and development.
It is incumbent upon parents to acknowledge the processing apprehensions linked to ramen noodles and to temper their children's intake of this food. Abundant healthier alternatives exist, presenting equal ease of preparation and superior nutritional merit.
Here are some directives for parents aiming to curtail their children's ramen noodle consumption:
- Establish limitations on the frequency of ramen noodle consumption.
- Offer healthier alternatives, such as whole-wheat pasta or brown rice.
- Ensure ample consumption of fruits, vegetables, and lean protein.
- Engage in discussions regarding the importance of a balanced diet.
Ramen noodles, a widely consumed food, especially among children, are appreciated for their affordability, ease of preparation, and delectable flavor. However, concerns exist regarding their potential health repercussions, primarily their elevated sodium content and the incorporation of various additives.
Ramen noodles encompass an assortment of additives, including preservatives, flavor enhancers, and coloring agents. Certain additives have been correlated with health concerns. For instance, specific preservatives have been linked to oncogenesis, whereas certain flavor enhancers have been associated with obesity and related health issues. Coloring agents have also been implicated in diverse health adversities, including allergies and hyperactivity.
The long-term ramifications of consuming these additives remain incompletely elucidated. Nevertheless, it is essential to acknowledge the potential health risks and moderate children's ramen noodle intake.
Here are some recommendations for parents seeking to mitigate their children's ramen noodle consumption:
- Set limitations on the frequency of ramen noodle consumption.
- Offer healthier alternatives, such as whole-wheat pasta or brown rice.
- Ensure ample consumption of fruits, vegetables, and lean protein.
- Engage in discussions regarding the importance of a balanced diet.
Ramen noodles, a favored food item, particularly among children, are lauded for their cost-effectiveness, convenience, and palatability. Nevertheless, apprehensions arise concerning their potential health implications, notably their elevated sodium content, additive incorporation, and portion size.
- Overeating: Ramen noodles are typically packaged in substantial quantities, potentially inducing overconsumption and amplifying the risk of excessive sodium and unhealthy ingredient intake.
- Obesity: Excessive ramen noodle consumption can foster weight accrual and obesity, a major precursor to cardiovascular disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and other chronic morbidities.
- Malnutrition: Ramen noodles possess limited nutritional value, and excessive consumption can precipitate malnutrition, characterized by inadequate nutrient intake.
- Other health problems: Excessive sodium consumption can engender hypertension, kidney disease, and other health complications.
It is imperative for parents to recognize the potential health adversities linked to excessive ramen noodle consumption. Parents should judiciously regulate their children's ramen noodle intake and proffer healthier substitutes, such as whole-wheat pasta or brown rice.
Ramen noodles, a cherished food option, particularly among children, are valued for their affordability, ease of preparation, and satisfying taste. Nonetheless, disquiet persists regarding their potential health ramifications, notably their elevated sodium content, presence of additives, substantial portion size, and targeted marketing towards children.
Ramen noodles are frequently marketed towards children through vibrant colors, engaging shapes, and iconic cartoon characters. This promotional strategy may lead children to perceive ramen noodles as a wholesome and enjoyable food choice. However, this perception is incongruent with reality. Ramen noodles are replete with sodium, deficient in essential nutrients, and often laden with deleterious additives. Excessive consumption of ramen noodles can engender a spectrum of health predicaments, encompassing obesity, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.
It is incumbent upon parents to remain cognizant of the marketing ploys employed by food conglomerates to engage children. Parents should apprise their children of the importance of embracing a balanced diet and making conscientious dietary decisions. Furthermore, parents should curtail their children's exposure to marketing campaigns promoting unhealthy foods, such as ramen noodles.
The marketing of ramen noodles towards children constitutes a substantive concern. This promotional approach can engender the erroneous belief that ramen noodles represent a healthy food option, while in truth, they do not. Parents should remain informed about this marketing tactic and engage in open dialogues with their children regarding the significance of adhering to a healthful dietary regimen.
There is some concern that ramen noodles may not be as healthy as they seem. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about the potential dangers of ramen noodles:
Question 1: Are ramen noodles really dangerous?There is no scientific evidence to support the claim that ramen noodles can cause death. However, ramen noodles are high in sodium and low in nutrients. Consuming too much sodium can lead to high blood pressure, which is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke. Eating too many ramen noodles can also lead to malnutrition.
Question 2: How much sodium is in a serving of ramen noodles?A single serving of ramen noodles can contain up to 1,000 milligrams of sodium. This is more than half of the recommended daily intake for adults and children over the age of 14. Children under the age of 14 should consume even less sodium.
Question 3: What are the other health risks associated with eating ramen noodles?In addition to high blood pressure and malnutrition, eating too many ramen noodles can also lead to obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. Ramen noodles are also often high in unhealthy fats and calories.
Question 4: Are there any healthy alternatives to ramen noodles?Yes, there are many healthy alternatives to ramen noodles. Some healthier options include whole-wheat pasta, brown rice, and quinoa. These foods are all low in sodium and high in fiber and nutrients.
Question 5: How can I reduce my child's intake of ramen noodles?There are a few things you can do to reduce your child's intake of ramen noodles. First, set limits on how often your child can eat ramen noodles. Second, offer your child healthier alternatives to ramen noodles, such as whole-wheat pasta or brown rice. Third, make sure your child is getting plenty of fruits, vegetables, and lean protein in their diet.
Question 6: What are the key takeaways about the dangers of ramen noodles?The key takeaways about the dangers of ramen noodles are that they are high in sodium, low in nutrients, and can lead to a number of health problems, including high blood pressure, heart disease, obesity, and diabetes. Parents should limit their children's intake of ramen noodles and offer them healthier alternatives.
If you are concerned about the health risks associated with eating ramen noodles, talk to your doctor or a registered dietitian.
Transition to the next article section:
While there is no scientific evidence to support the claim that ramen noodles can cause death, there is some concern that they may not be as healthy as they seem. Ramen noodles are high in sodium and low in nutrients. Consuming too much sodium can lead to high blood pressure, which is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke. Eating too many ramen noodles can also lead to malnutrition.
Parents should be aware of the potential health risks associated with eating ramen noodles and limit their children's intake of this food. There are many other healthier options available that are just as easy to prepare and more nutritious.
- Guide Watch Kannada Movies Online Is 5movierulz Kannada Safe
- Deon Cole Is Deon Cole Married Spouse Career More

Family Is Left Devastated When Five Kids Died After Eating INSTANT

Five Kids Die After Eating Instant Noodles, Family Of Latest Victims
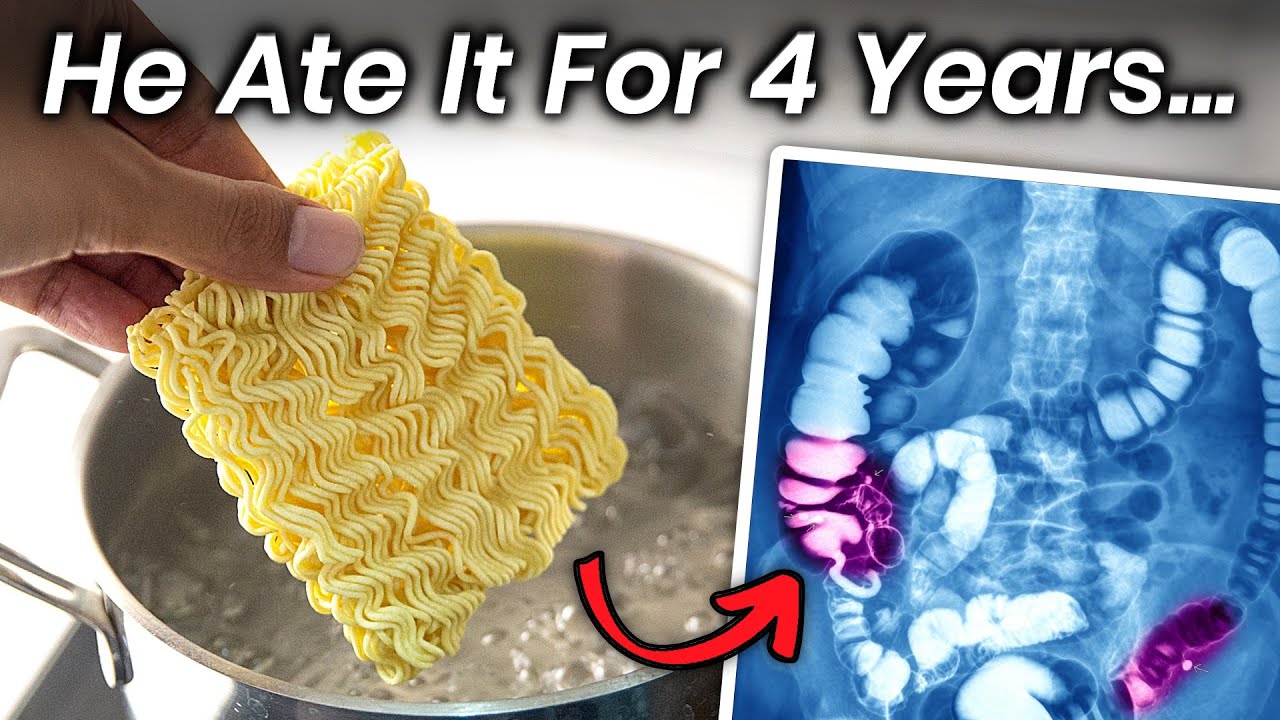
A Boy Ate Instant Noodles for 4 Years, This Is What Happened to His